One of the things the World should thank India for | The USB Port
You see it in your laptops whether old or new not the ancient ones, in your phones, in your storage devices, sometimes in your broadband or router, in your wifi dongle, in your keyboard, mice, and other peripherals, literally everywhere. So, what is it, that's exactly what we are going to cover in this post.
Where it all started ?
The first USB which stands for Universal Serial Bus technology began development in 1994, co-invented by Ajay Bhatt of Intel and the USB-IF (USB Implementers Forum, Inc). The organization is comprised of industry leaders like Intel, Microsoft, Compaq, LSI, Apple, and Hewlett-Packard. It supports and adopts comprehensive specifications for all aspects of USB technology.Before the invention of USB, computers used serial ports, those which had pins and stuff, for example, the DVI ports and the VGA ports. Individual ports were used for peripherals such as keyboards, mice, joysticks, and printers. Talking about their transfer rates, the speed ranged from 110 KB/s to 450 KB/s
which was nowhere close to even the oldest modern-day ports.
The first USB, USB 1.0 debuted in late 1995 and transferred data at a rate of 12 MB/s. A revised version of this standard, USB 1.1, not only transferred data at a full-speed rate of 12 MB/s but could also operate at a lower speed of 1.5 MB/s for lower bandwidth devices. Due to its more efficient operation, USB 1.1 was used more by consumers than its predecessor.
What was ahead ?
With a transfer rate 40 times faster at 480 MB/s, USB 2.0 debuted in 2000 and became an official standard the following year. In addition to this, USB 2.0 was capable of operating at 2 slower speeds: 12 MB/s and 1.5 MB/s. A USB 2.0 port will function with USB 1.1 devices, although a USB 1.1 port may not have the bandwidth capabilities to properly communicate with a 2.0 device.
USB 2.0 offers plug and play capabilities for various multimedia and storage devices. This newer version offered additional user features that did not exist in its previous version. USB 2.0 added support for power sources with USB connectors, a new descriptor for multiple interfaces, as well as the capability for two devices to interact without the need for a different USB host.

The year 2000 also introduced the USB flash drive—a rewritable plug-and-play storage device first sold by IBM and Trek Technology. It could initially hold up to 8 GB of data. More than a decade later, storage capacities have surpassed 256 GB for a single drive.
The year 2000 also introduced the USB flash drive—a rewritable plug-and-play storage device first sold by IBM and Trek Technology. It could initially hold up to 8 GB of data. More than a decade later, storage capacities have surpassed 256 GB for a single drive.
It's current technology :
USB 3.0 is the third major version of the Universal Serial Bus (USB) standard for interfacing computers and electronic devices, which was released in November 2008. USB 3.0 adds the new transfer rate referred to as SuperSpeed USB (SS) that can transfer data at up to 5 Gbit/s, which is about 10 times faster than the USB 2.0 standard.
USB 3.1, released in July 2013, is the successor standard that replaces the USB 3.0 standard. USB 3.1 preserves the existing SuperSpeed transfer rate, giving it the new label USB 3.1 Gen 1, while defining a new SuperSpeed+ transfer mode, called USB 3.1 Gen 2, which can transfer data at up to 10 Gbit/s over the existing USB3-type-A and USB-C connectors (1250 MB/s, twice the rate of USB 3.0)
USB 3.2, released in September 2017, replaces the USB 3.1 standard. It preserves existing USB 3.1 SuperSpeed and SuperSpeed+ data modes and introduces two new SuperSpeed+ transfer modes over the USB-C connector using two-lane operation, with data rates of 10 and 20 Gbit/s (1250 and 2500 MB/s).
It's types:
There are manly 4 types for each version of the USB:
USB 2.0 :
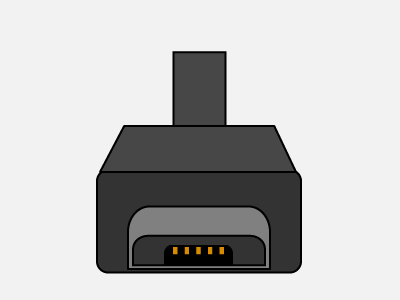 Type-B Micro
Type-B Micro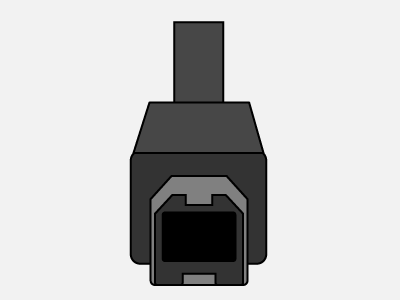 Type-B
Type-B Type-A
Type-A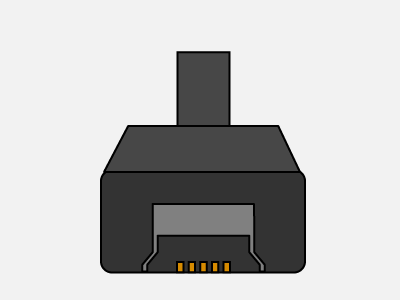 Type-B Mini
Type-B Mini- USB Type-A (The standard USB port which we see in our laptops, etc)
- USB Type-B (Used in digital cameras, external hard drives, USB hubs, etc)
- USB Type-B mini (Also used in digital cameras, external hard drives, USB hubs, etc)
- USB Type-B micro (used in your android phones)
USB 3.0 :
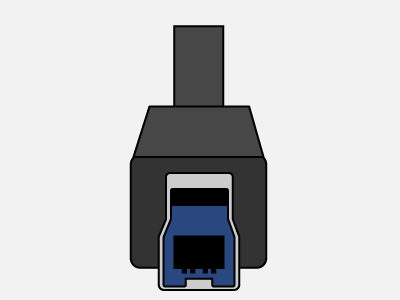 Type-B
Type-B Type-B Micro
Type-B Micro Type-A
Type-A Type-C
Type-C- USB Type-A (The standard USB port which we see in our laptops, etc)
- USB Type-B micro (A different one, used in storage devices and power units)
- USB Type-B : (Used in digital cameras, external hard drives, USB hubs, etc)
- USB Type-C : ( One of the fastest USBs speed from 4 Gb/s to 10 GB/s)
Ajay V. Bhatt is an Indian-born American computer architect who defined and developed several widely used technologies, including USB, AGP, PCI Express, Platform Power management architecture, and various chipset improvements. After completing his graduation from the Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, India, Bhatt received his master's degree from The City University of New York, United States.
Bhatt joined Intel in 1990 as a senior staff architect on the chipset architecture team in Folsom. He holds 132 U.S. and international patents, and several others are in various stages of filing. In 1998, 2003, and 2004, Bhatt was nominated to take part in a Distinguished Lecture Series at leading universities in the United States and Asia. He received an Achievement in Excellence Award for his contribution to PCI Express specification development in 2002.

Nice information, will help in my GK exam
ReplyDeleteI was going to give a very long and nice suggestion and I wrote it and when I clicked publish sadly it gave an error :( and now its gone so I'll write again and post later
ReplyDeleteGreat job Maulik
ReplyDeleteWhat about thunderbolt?
ReplyDeleteHi bro, its been so long since you posted anything so just wanted to know when r u publishing ur next blog and why u not replying on telegram?
ReplyDelete